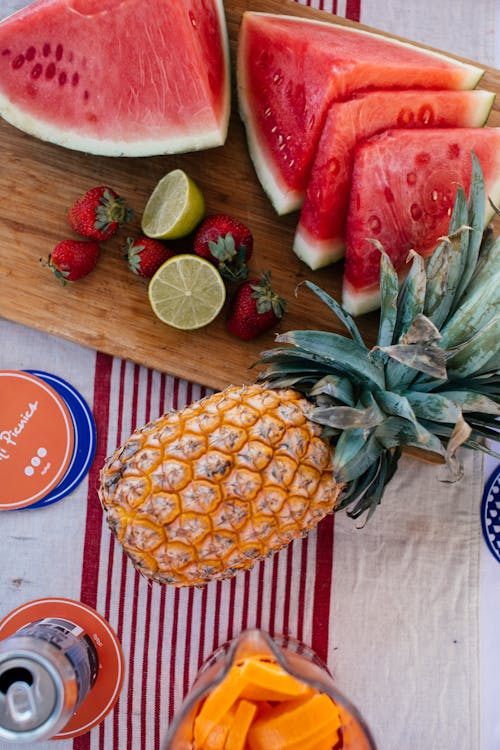
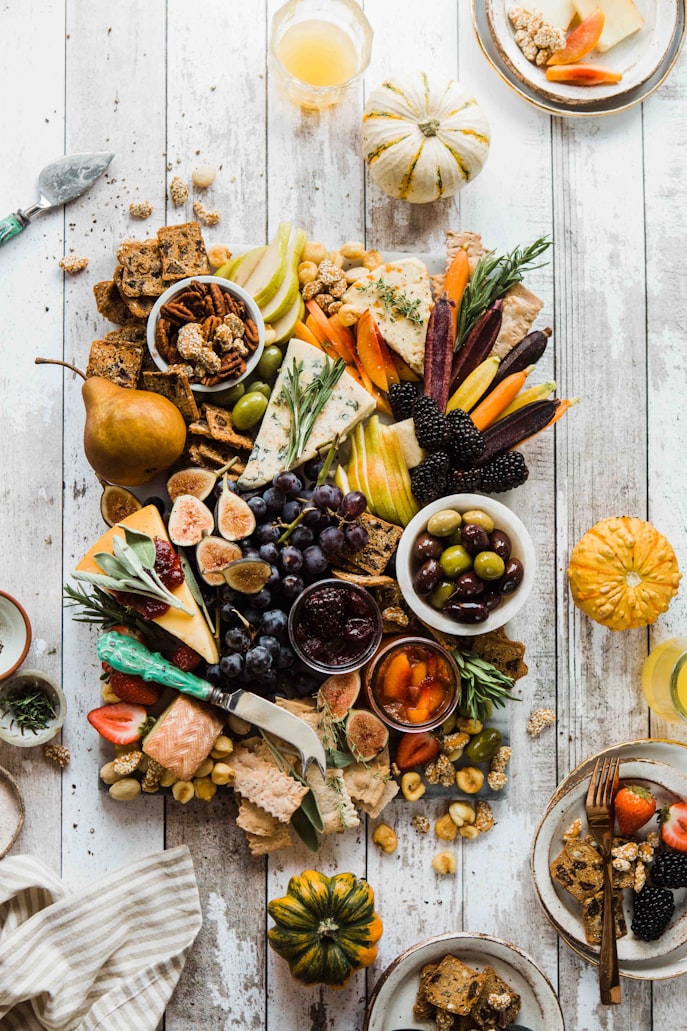
For those of us living with inflammation, the first cool breath of fall can feel like medicine.
After months of heavy heat, the air softens. The light turns golden. Nature seems to exhale … wrapping us in a palette of rust, amber, and cinnamon that reminds us to slow down and root ourselves again.
And just as the world shifts, so does what it offers.
Fall brings a harvest of ingredients that comfort and restore … foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and phytonutrients that help calm inflammation and steady blood sugar while still feeling hearty and satisfying.

There really is no shortage of sources of superfoods for those of us following an anti-inflammatory diet.

The beauty of this season is that even as summer’s abundance fades, the markets are still overflowing with anti-inflammatory staples. From earthy root vegetables to crisp apples and immune-supporting herbs, it’s a time to eat deeply … to choose warmth, grounding, and color on your plate.
Here are three of my favorite categories to focus on as the temperatures drop:
- Veg and Fruits: grounding, fiber-rich, and full of protective antioxidants
- Herbs: fragrant plant medicine that supports digestion and immunity
- and Spices: warming allies that keep circulation flowing and inflammation quiet
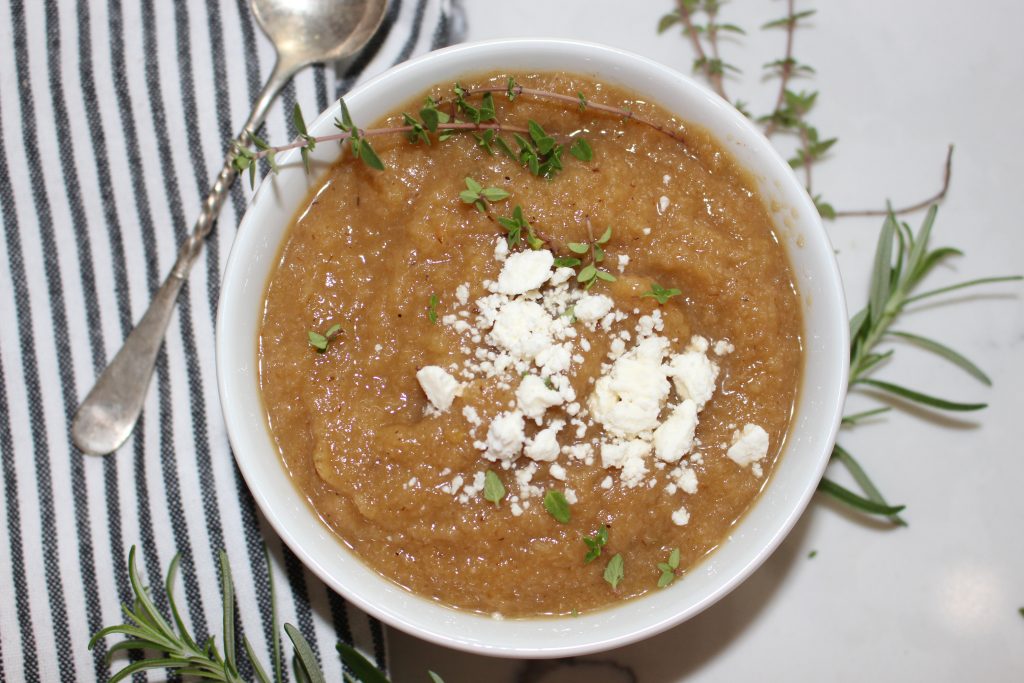
Here are my favorites that make fall feel (and taste) like healing.
Veg and Fruits

WANT MORE FALL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEALS? CHECK OUT THE FALL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEAL PREP SESSION! (4+ MEALS –> PERFECT FOR CRAZY WEEKS WITH NO TIME TO MEAL PLAN!) CLICK HERE TO READ MORE
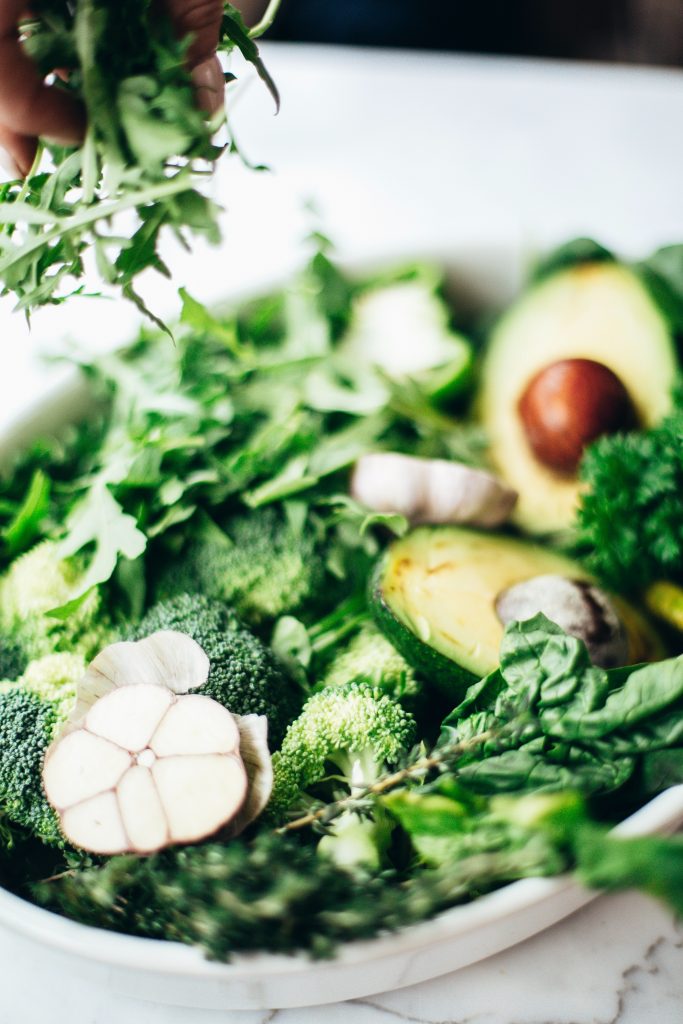
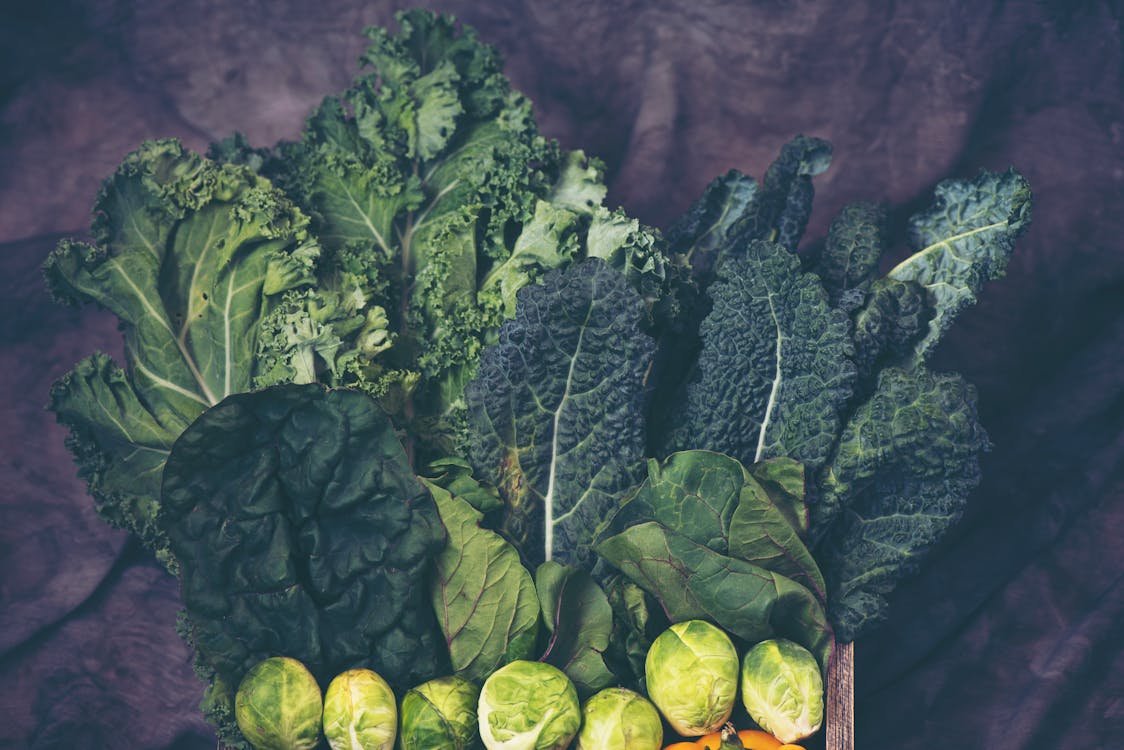
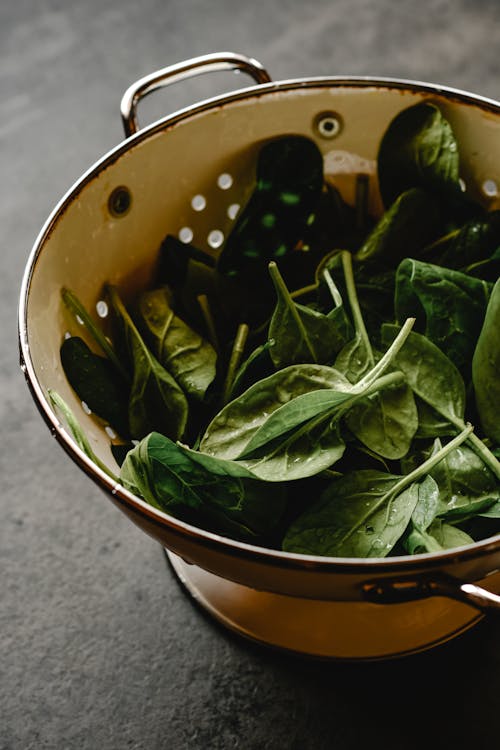
Leafy Greens
Even though leafy greens start their appearance in the summer, fall leafy greens follow with even more flavor!
Greens like kale, arugula, collard greens, and swiss chard are packed full of vitamins and antioxidants. And they’re versatile enough that many can be eaten raw, cooked, as a stand-alone side, or even as a soup or casserole component.
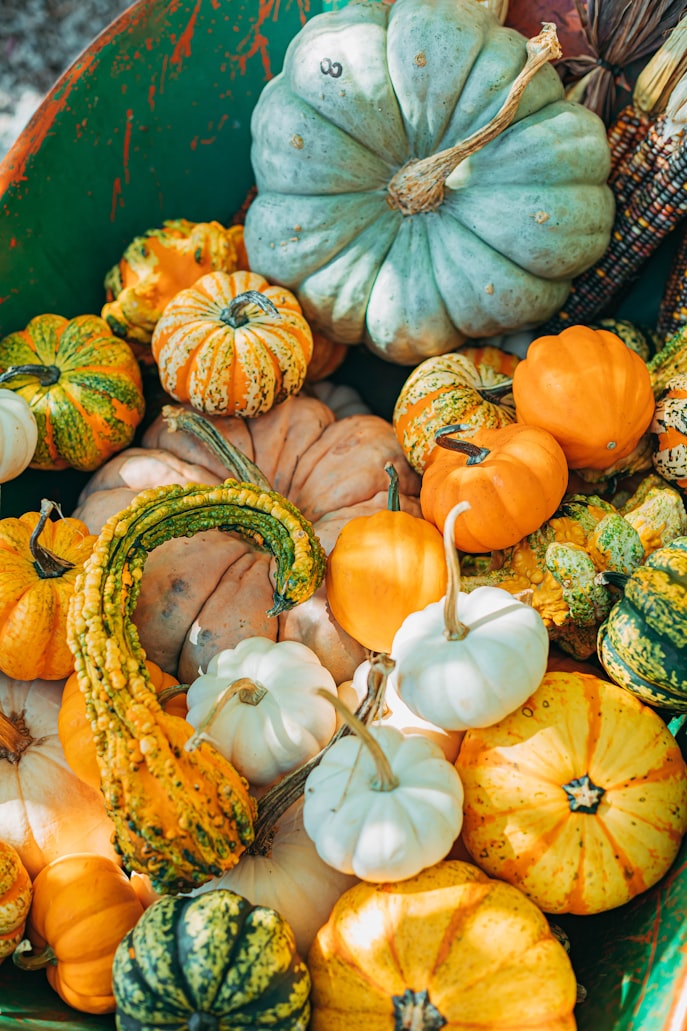

Pumpkins
Arguably the most popular fall vegetable, pumpkins provide an amazing source of Vitamin A (the color gives you that hint on beta carotene), balanced polyunsaturated fats, Vitamins C and E, and several other essential minerals.
They’re also packed with fiber and healthy carbs, and can be stored for a long period of time (in a dry pantry or frozen) without going bad.
Butternut Squash
Butternut squash is also packed with Vitamin A, but it’s also an amazing source of Vitamin C as well. Compared to pumpkins, it’s more dense in energy, meaning: per serving it contains more calories, carbs, and fiber.
What I love about butternut squash is that it’s flavor makes more amazing soups. But it’s versatile enough to serve in cubes as a side dish (or in a casserole), or as a substitute for potatoes if you’re looking for a lower carb alternative.
No meal plan this week? No problem! Grab the (free!) FALL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEAL PREP GUIDE! Click HERE or the image above!

Sweet Potatoes and White Potatoes
Sweet potatoes also have a ton of Vitamin A. But aside from that, their nutritional value is nearly the same as white potatoes. And even though white potatoes have more carbs, this occurs as starches versus the sugar content in sweet potatoes, which is something to consider if you’re watching your blood sugar levels.
Either are great options for soups or even just sliced and baked as healthier fries.

Beets
One of the most overlooked vegetables (in my opinion) is the beet. Beets are high in folate and manganese, but also contain betalains, which gives it the bright red color, and is associated with reduced cancer risk.
Not only can you eat the beet itself, but the greens are also a fantastic source of nutrition. Beets can be roasted, sauteed, pickled, or boiled; and the greens can be used in salads or saved for soup broths.

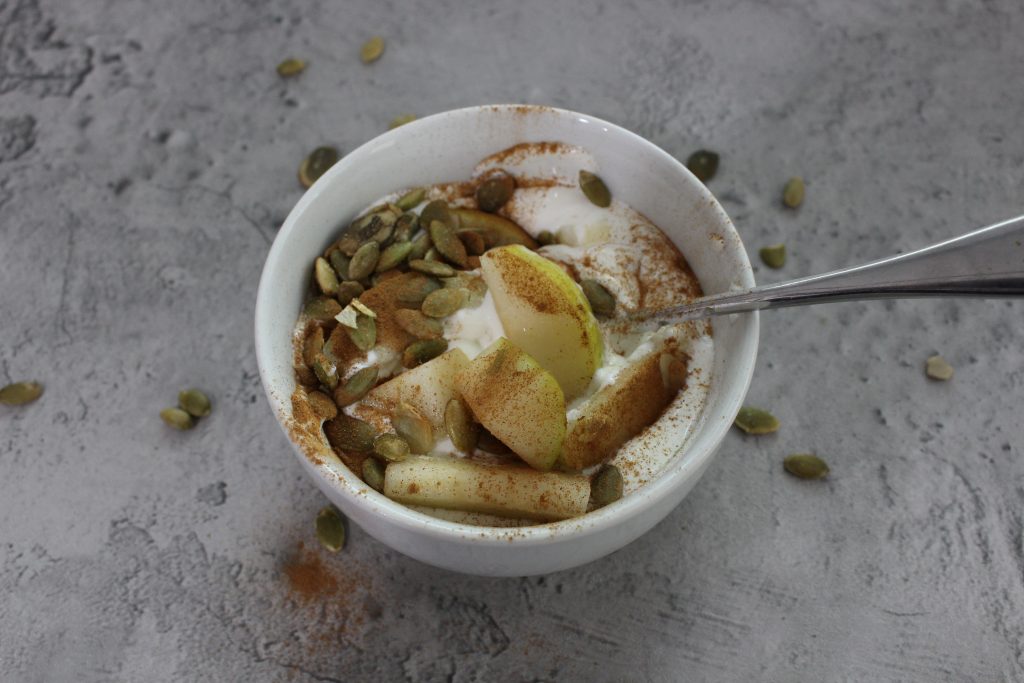
Apples
Ahhh…the quintessential fruit for fall! Apples peak season is September, so take advantage of this amazing time of year to get super fresh apples! The best way to eat them is raw, as fresh as possible, and with the skin on.
Not only do apples give tons of fiber, the skin contains quercetin, which is amazing for those with allergies, and it also reduces inflammation.
🌿 Want to know exactly which foods help lower inflammation year-round?
Grab the free Anti-Inflammatory Diet Quick-Start Guide. It’s your shortcut to understanding what to eat, what to skip, and how to balance your blood sugar without cutting everything you love.
👉 Download the Quick-Start Guide and start feeling the difference this week.
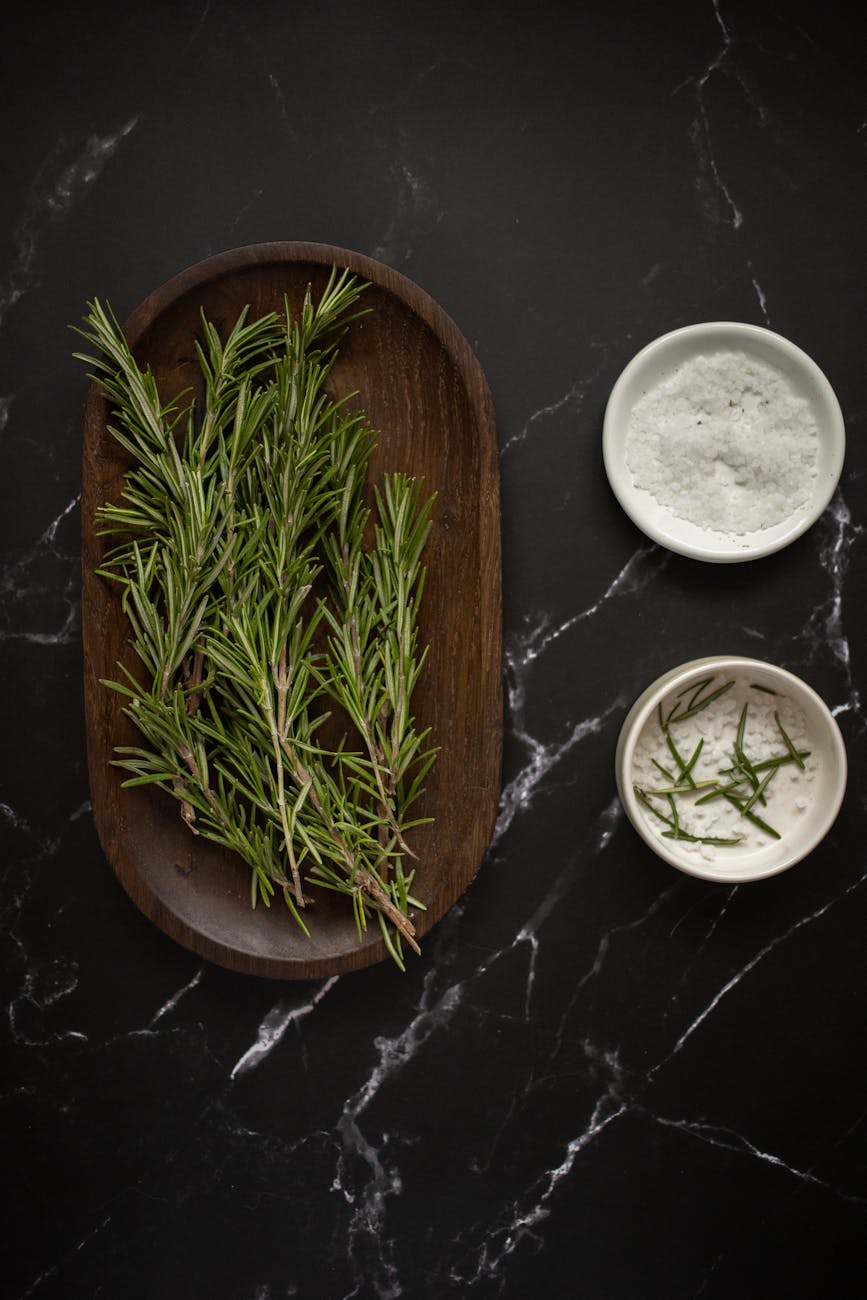
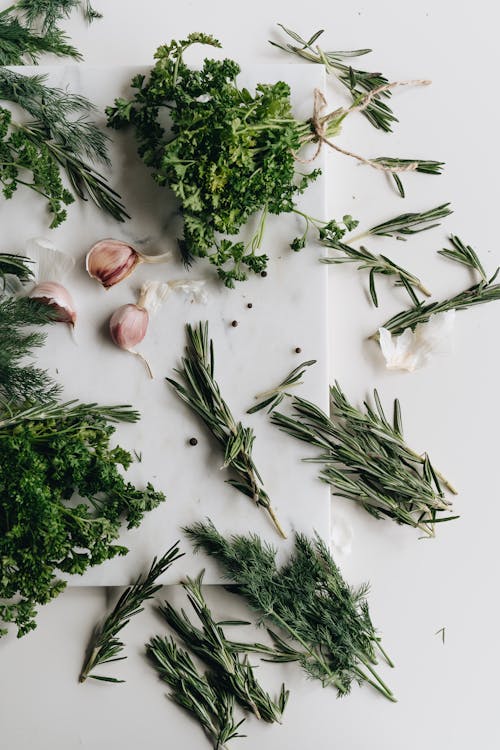
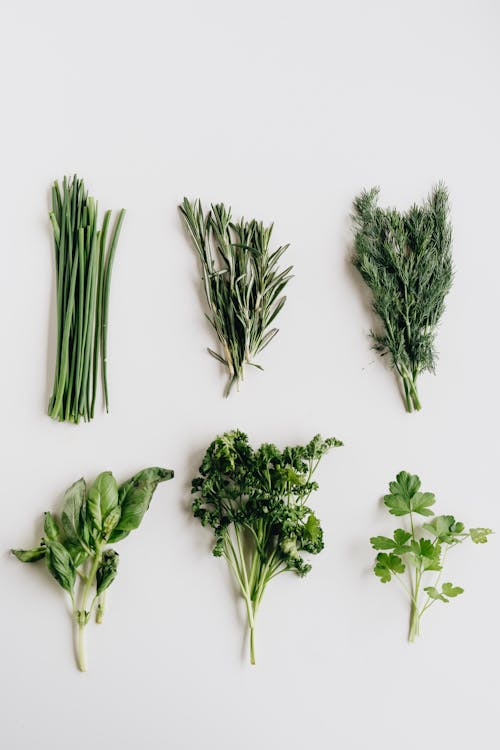
Herbs
Herbs are one of the most overlooked nutrition powerhouses in the plant family. They pack so much punch for such a little plant. But they’re also SO EASY to add in to any dish for extra flavor.
Here are my favorite anti-inflammatory herbs for fall.
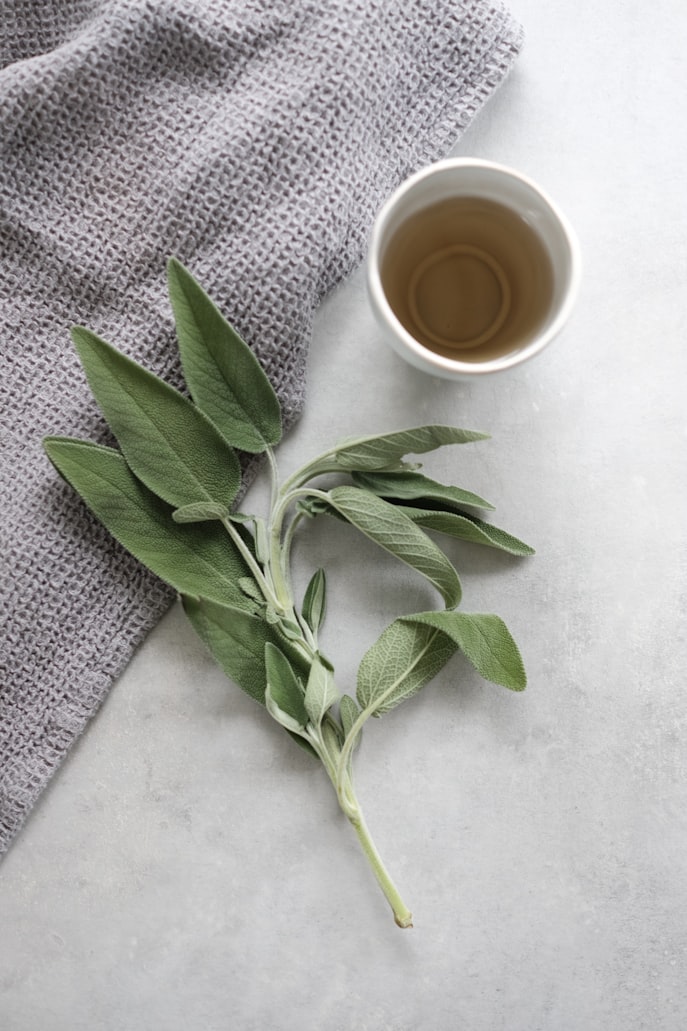

Sage
Sage not only adds delicious earthy notes to fall and winter dishes, but also can be used in teas and as an essential oil. Sage is high in Vitamin K and vital minerals, but also contains antioxidants.
What’s so amazing about sage is that it’s been shown to relieve or cure illnesses like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, depression, dementia, and lupus. But it’s also been used for centuries in traditional medicine for inflammation, bacterial, and viral infections, which makes it high on the list for cold and flu season.

Rosemary
Rosemary is full of iron, calcium, and vitamin B-6, and is also native to the Mediterranean—fitting for an anti-inflammatory diet rooted in the Mediterranean diet. It’s been used for a wide range of ailments including digestion, muscle pain, improved circulation and memory, and a boost to the immune system.
Aside from its fragrant and mouthwatering culinary powers, studies have proven its anti inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and neuroprotective properties. This means that even though it can fight free radicals and harmful bacteria, it can also be used in mood disorders, enhanced learning, anxiety, and sleep disorders.

Thyme
Thyme (another herb native to the Mediterranean) can be used as a treatment for anything from acne to GI disturbances to menstrual cramps (and a ton of stuff in between!) But it’s actually an extremely versatile culinary addition. It has an earthy flavor but can waver back and forth between savory or sweet dishes like stocks and stews, roasted vegetables, teas, and desserts.
Fall Spices
Although spices can generally be used year-round, the warmth of the following three are perfect for the cooling weather.
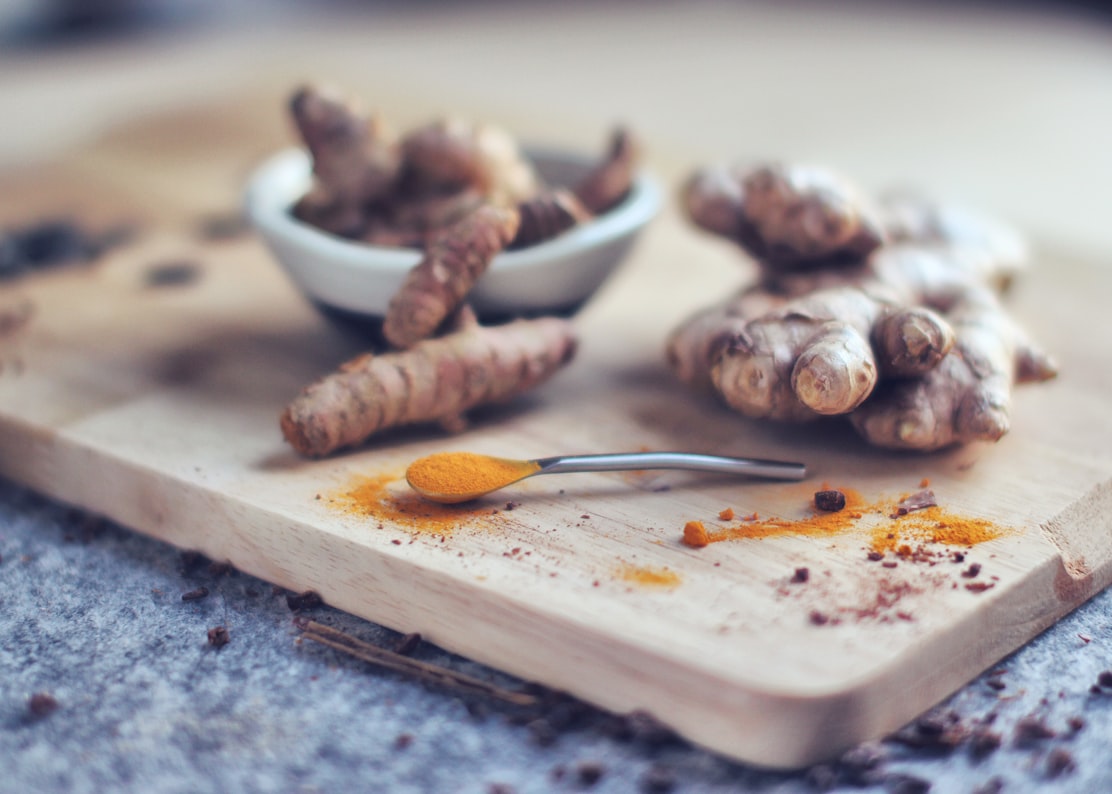

Ginger
Ginger has been touted to help anything from boosting the immune system, lowering blood sugar, and easing inflammation. Probably it’s most famous claims to fame include taming the GI tract and pulling down inflammation. These benefits are made possible due to the over 400 compounds that ginger contains.
Ginger has a fresh, zingy flavor, and although the dried version (teas and spice shakers) have a milder flavor than fresh, they can still have nearly the same health benefits. It’s best to use fresh, and ginger root can be cut up and put in the fridge or frozen to last even longer.
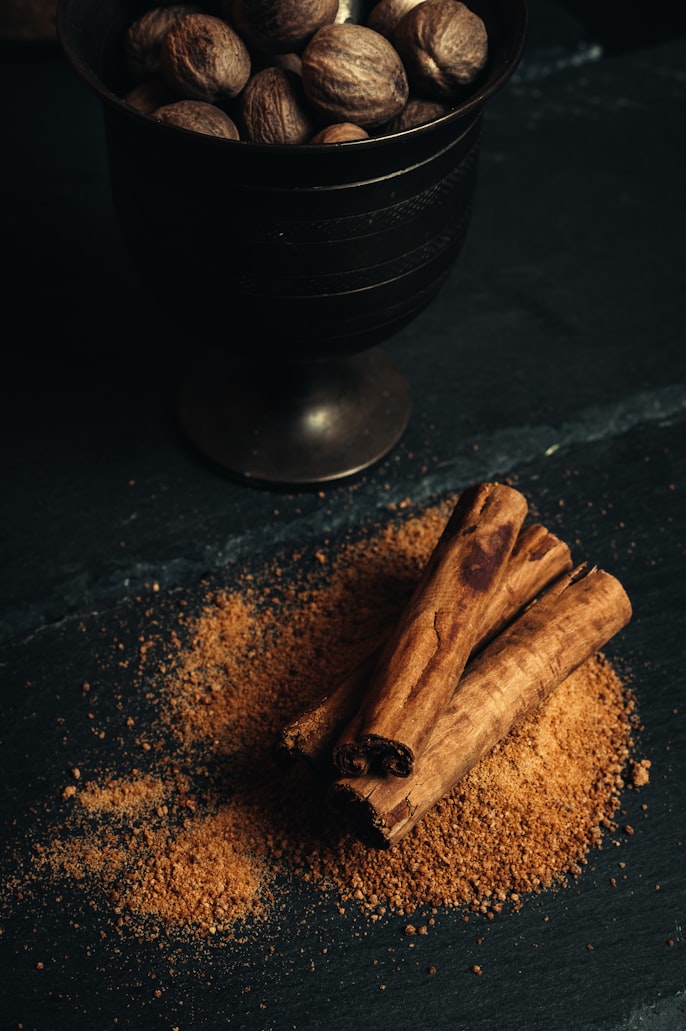

Cinnamon
There can be a lot of confusion over the type of cinnamon that’s best to use. Ceylon (known as ‘true’ cinnamon) and cassia (what you buy in the grocery store) are equally delicious and contain a compound called cinnamaldehyde that’s thought to be responsible for its health and metabolism benefits.
Cinnamon has been shown to contain more antioxidant activity than any other in a study against 26 other spices, is a potent anti-inflammatory, and has been shown to reduce insulin resistance (among other benefits).
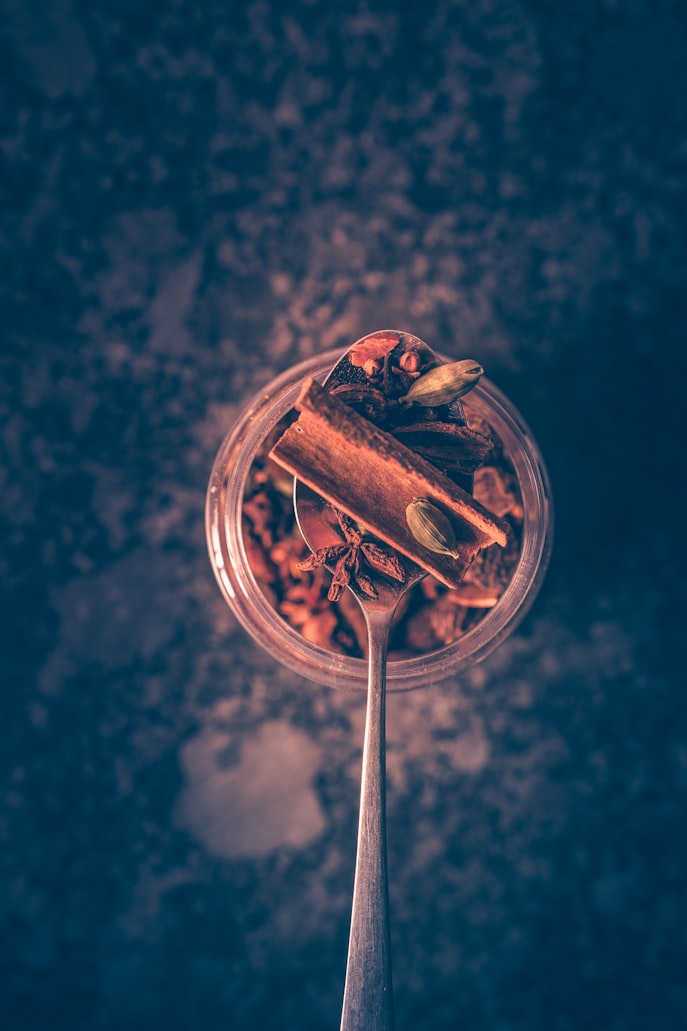

Pumpkin pie spice
Honestly my favorite spice for fall is a combination of several spices: Pumpkin pie spice. This mixture obviously enhances pumpkin flavor, but can be used in a variety of recipes in fall and winter.
The components of pumpkin pie spice include cinnamon and ginger, which we already covered. The other ingredients are nutmeg, cloves, allspice, and black pepper.
What’s so great about the blend in pumpkin pie spice is that all the ingredients have powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds just like the other spices mentioned.
So as long as you use healthy sweeteners and anti-inflammatory ingredients for whatever pumpkin spice recipe you’re making, you essentially have a superfood recipe with powerhouse ingredients for fall!
Fall is the perfect season to reset your plate — but knowing where to start makes all the difference.
My free Anti-Inflammatory Diet Quick-Start Guide walks you through the exact first steps to reduce inflammation, stabilize energy, and feel amazing without the overwhelm.
🍎 Get your free Quick-Start Guide here and start building your anti-inflammatory lifestyle today.
Let me know in the comments: What’s YOUR favorite anti-inflammatory fall food or recipe?
Click the image below to grab the Fall Anti-Inflammatory Meal Prep Guide! 👇
📌PIN IT FOR LATER!










 QUICK-START GUIDE!
QUICK-START GUIDE!